Crown lengthening
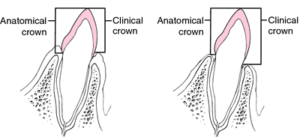
# Clinical crown : crown visible in oral cavity
# Anatomic crown : incisal edge till CEJ
# Active eruption : when tooth erupts into oral cavity and reaches to occlusal level
# Passive eruption : gingival recessing down to CEJ when the tooth finish erupting
3 things to take note in crown lengthening: biologic width, crown :root ratio, ferrule effect
Indications of crown lengthening
- Treatment of subgingival caries, crown or root fractures, altered passive eruption
- Cervical root resorption
- Short clinical abutment (to provide retention for proper tooth prep)
- To produce ferrule for restoration
- To access perforation in coronal ⅓ of root
- To adjust gingival level for esthetics (gummy smile)
- To relocate the margins of restorations that are impinging on biologic width (pt will complain gums keep bleeding)
- Short teeth for esthetics
Contraindications
- Inadequate crown :root ratio
- Non restorable caries/root fracture
- Esthetic compromise (black triangles)
- High furcation (when molars has furcation quite coronally located)
- Sensitivity
- Tooth arch relationship inadequacy (occlusal space)
Restorative considerations :
- Esthetic demand
- Function (posterior teeth – mastication)
- Form
- Retention
- Marginal seal
| Clinical analysis | Radiographic analysis |
| Sulcus depth, Biologic width
Osseous crest Pulp involvement Apical extend of # Amount of attached gingiva and gingival health Furcation location Loss of mesial distal or occlusal space Anticipated final margin placement Lip line (at rest and smile line) |
Level of alveolar crest
Apical extent of caries Pulpal involvement Furcation Root trunk length (distance between CEJ till furcation area) Crown to root ratio |
2 methods of clinical crown lengthening
- Extension apically : apically positioned flap, gingivectomy
- Extension coronally :orthodontic/ surgical extrusion, post and core
- Combination of both
Biologic width : distance between depth of gingival sulcus till crest of alveolar bone :2.04mm
So, considering 1mm of gingival sulcus + 2mm of biologic width → the distance between margin of restoration till crest of bone should be 3mm
** margin placement cannot be more than 0.5mm into the gingival sulcus to avoid damage to biologic width
If there is violation of biologic width : either tissue respond by gingival inflammation & pocket formation OR self adjustment by body with alveolar bone loss to form back own biologic width
Evaluation of biologic width
- Clinical method
-presence of tissue discomfort when you use probe to go around the margin of restoration
-look for signs (BOP, gum inflammation, gum recession,pocket, CAL, alveolar bone loss)
- Radiographical method
- Bone sounding / Transgingival probing
-under LA, insert probe till crest of bone and minus sulcus depth.
-if <2mm → violation of biologic width
Presurgical analysis:
-determine finishing line (if cannot determine, should anticipate where it is)
-Do bone sounding before surgery to establish biologic width
Treatment :
a)gingivectomy only (using electrosurgery/laser)
-if there is enough amount of sulcus depth and attached gingiva above the crestal bone
-if there is 3mm pocket and then 2mm from base of pocket till crest of bone, so can just do gingivec
b)internal bevel gingivectomy with or without ostectomy
-when there is enough attached gingiva after incision made
c)apical repositioning of flap with or without ostectomy
–** done when there is less than adequate attached gingiva
-you wont be removing the gingiva but will just place it more below and remove the bone
d)surgical/orthodontic repositioning
-when do gingivectomy, the gingival margins will be not harmonious causing bad esthetics
-when there will be furcation involvement after CLP
-will need time, no tooth for some time
-C/I when inadequate anchorage to perform ortho extrusion
Cx of crown lengthening
-poor esthetics (black triangles)
-root sensitivity
-root resorption
-transient mobility of teeth
-gingival retraction (change in gingival contour)
-crown root ratio is unfavourable
-furcation involvement

When can we give final restorations?
-6-8 weeks , provided the maintanence of pt is good, no more inflammation
#When pt say she has redness of gums → have to evaluate whether there is poor maintanence/ violation of biologic width – remove the crown – place a temporary crown to allow area to heal for 2 weeks – reassess biologic width – if there is less distance from gingival margin to crest of bone → then will need to remove the bone to form back biologic width
When to give temporary restoration?
- Intraoperative (If there is less height of tooth achieved after crown lengthening, give intraoperative temp to prevent the rebound of gingiva → so that even gum rebounds, it will rebound about the margin of temp crown)
- Early
- Delayed (if there is adequate height that is achieved, no need worry about gingiva rebound even if it occurs. Can wait for 2-3 weeks then give temp crown. Then can recall pt after 3-5 weeks to assess the healing of the area, if is ok. Then, can take imp and give permanent crown.
If supposed to place margins subgingivally,should have
-Correct crown contour in gingival ⅓
-Correct polishing and rounding of margins
-Sufficient zone of attached gingiva
-No biological width
